Difference between revisions of "WordPress Setup"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Recommended WordPress Toolkit Settings == | == Recommended WordPress Toolkit Settings == | ||
=== Updates === | |||
[[File:WP-Toolkit-Update-Settings.png|thumb|right|alt=WP Toolkit Update Settings|Update Settings]] | |||
Recommended update settings for WordPress core, plugins, and themes: | |||
* Update WordPress automatically | |||
** Yes, but only minor (security) updates: With this setting you will only get security updates automatically and will have to install major/feature updates yourself. This is the absolute minimum recommended setting. | |||
** Yes, all (minor and major) updates: With this setting all updates will be installed. You will need to check your site after a major update to make sure nothing has been broken by the update. If you have a simple site without many 3rd party plugins or themes this is recommended. | |||
* Update plugins automatically | |||
** Defined individually, but security updates are autoinstalled: | |||
** Forced: | |||
* Update themes automatically | |||
** Defined individually, but security updates are autoinstalled: | |||
** Forced: | |||
Enact the following WP Toolkit Security recommendations (at a minimum):[[File:Recommended-Minimum-Security-Settings.png|thumb| | === Minimum Security === | ||
Enact the following WP Toolkit Security recommendations (at a minimum):[[File:Recommended-Minimum-Security-Settings.png|thumb|right|alt=Recommended Security Settings|Recommended Security Settings]] | |||
* Restrict access to files and directories | * Restrict access to files and directories | ||
* Block directory browsing | * Block directory browsing | ||
| Line 21: | Line 33: | ||
* Block access to .htaccess and .htpasswd | * Block access to .htaccess and .htpasswd | ||
Enact these security settings in addition to the above:[[File:Preferred-Security-Settings.png|thumb| | === Recommended Security === | ||
Enact these security settings in addition to the above:[[File:Preferred-Security-Settings.png|thumb|right|alt=Preferred WordPress Toolkit Security Settings|Preferred Security Settings]] | |||
* Configure security keys | * Configure security keys | ||
* Disable scripts concatenation for WordPress admin panel | * Disable scripts concatenation for WordPress admin panel | ||
Revision as of 17:05, 27 March 2022
WordPress Best Practices
- Keep Wordpress Core and all plugins and themes updated
- Remove all unused plugins and themes
- Practice good password hygiene
- Use strong passwords
- Do not reuse passwords
- Enable two-factor authentication where possible
- Use a trusted password manager such as 1Password
Recommended WordPress Toolkit Settings
Updates
Recommended update settings for WordPress core, plugins, and themes:
- Update WordPress automatically
- Yes, but only minor (security) updates: With this setting you will only get security updates automatically and will have to install major/feature updates yourself. This is the absolute minimum recommended setting.
- Yes, all (minor and major) updates: With this setting all updates will be installed. You will need to check your site after a major update to make sure nothing has been broken by the update. If you have a simple site without many 3rd party plugins or themes this is recommended.
- Update plugins automatically
- Defined individually, but security updates are autoinstalled:
- Forced:
- Update themes automatically
- Defined individually, but security updates are autoinstalled:
- Forced:
Minimum Security
Enact the following WP Toolkit Security recommendations (at a minimum):
- Restrict access to files and directories
- Block directory browsing
- Block unauthorized access to wp-config.php
- Disable PHP execution in cache directories
- Block access to sensitive files
- Forbid execution of PHP scripts in the wp-includes directory
- Forbid execution of PHP scripts in the wp-content/uploads directory
- Block access to .htaccess and .htpasswd
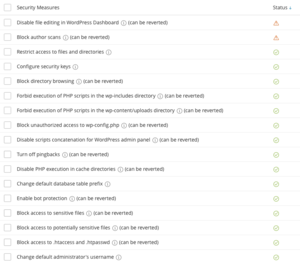
Recommended Security
Enact these security settings in addition to the above:
- Configure security keys
- Disable scripts concatenation for WordPress admin panel
- Turn off pingbacks
- Change default database table prefix
- Enable bot protection
- Block access to potentially seneitive files
- Change default administrator's username
Addon Domains
When setting up Addon domains (especially for Worpress installations) we recommend the Addon domains be placed outside your primary public_html folder. This helps prevent cross contamination of Wordpress installations if one of them gets infected with malware.